We are leading the market in the application of BIM software, tools, methods and processes in building engineering and construction sectors complying to the present project BIM requirements and precisely addressing business requisites without exceeding budgets and resources.
Tuesday, May 6, 2014
Monday, March 24, 2014
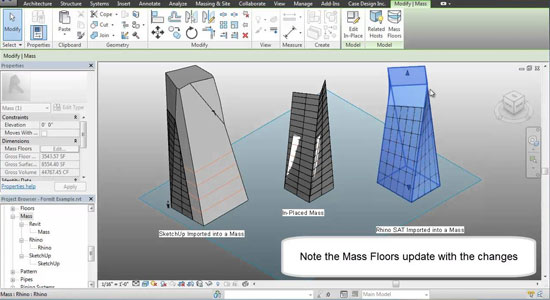
Revit 2014 - Working with Imported Solids and Temporary View Templates
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Published By
Tuhin Maity
www.bimoutsourcing.com
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Friday, February 21, 2014
IMAGINiT’s Scan to BIM 2014.1 Released

Thursday, May 24, 2012
Lumion launch free revit to Collada (.dae) exporter for real time architectural visualization
Process :-
~~~~~~~
For any 3D modeling services with BIM, Revit and Sketchup, please visit our site at www.bimoutsourcing.com and www.sketchup4architect.com
Friday, June 10, 2011
Combination of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and lean construction practices can enhance end-to-end design and construction process

BIM can be utilized together with lean construction practices for smoothing the work process for manufacturing, healthcare and other market sectors.
Model based lean approach deliver a huge cost saving in budget for owner as it significantly reduce waste and increase efficiencies throughout the life of the project.
It is a data rich work-planning tool that speed ups schedule and supports numerous downstream efficiency gains.
BIM with lean enabled workflows generate a comprehensive digital coordination process. The lean practice is very much useful for prefabricators as it helps to achieve levels of prefabrication. Fabricators are able to get large percentages of prefabrication on major components of the building systems.
Subcontractor can visually "prototype" all portions of their work in detail long before the commencement of fabrication or construction.
Lean construction practices is applied to solve the significant process issues like lack of time or money for full development, lack of training, lack of modeling standards or a lack of collaboration between stakeholders to the model.
Lean is a process improvement technology that provides an integrated project delivery approach towards a facility’s completion, identifying and then capturing huge opportunities to diminish waste, rationalize and drastically improve the end result.
A project team gets the ability to produce superior transparency, consistency and predictability in the quality of the work and reduction of material waste. Lean practices also reduce the waste in all its hidden form like defects, motion, inventory, transportation, overproduction, processing and waiting.
Posted by Rajib Dey
Business Development
rajib@jobs2india.com
Global Associates (Pioneer Company in 3D modeling with BIM & Sketchup)
visit our BIM sites
www.bimoutsourcing.com
www.bimcoordination.com
Sunday, May 22, 2011
BIM Coordination Guidelines

Now BIM is being utilized as a team concept by establishing a common understanding of what has to go into the model when it shifts from the design team to the construction team. This feature of BIM will lead to huge cost and time saving. Besides building conflicts can be easily found & fully coordinated and highly efficient buildings can be produced at significant cost savings.
There are design-review tools with unequal BIM platforms that maintain strong teaming environments and share the project vision among all stakeholders. The result comprises less risk for the team, the client, and the authorities having jurisdiction (AHJs), over and above safer, more effective structures for the owners and occupants.
In an integrated project delivery system the architect apply a BIM model; the (MEP) engineers contain a BIM model; and the structural engineer and other consultants may apply BIM as well. Then the contractor may utilize the model for phasing and sequencing the work. Major suppliers like the structural steel fabricator may utilize it to detail and fabricate building components. If possible, these “authoring tools” must be interconnected with the same applications or “flow” from the originating architect/engineer’s or owner’s BIM model.
Contractors and construction managers will have to assess the costs of various execution processes and deliver the results to owners and design teams in quantyfiable terms.
The 3D information should be distributed to the project team with accuracy. As for example if a designer presents an analysis model or 3D front wall rendering to supplement the design documents and the designer has stated that the analysis or rendering model cannot accurately show all aspects of the geometry, the designer should not be held liable in case a detailer pays no attention to the warning and supports the geometry on the supplemental model or rendering.
Design teams should allocate all available electronic information with the entire project team. Structural analysis models should be part of the design contract.
The designer should not compromise with the quality of the information. As for example, if the geometry or the load cases in a design model are partially inaccurate, this must be conveyed and documented with others. Additionally, the source of the correct information must be provided in the design documents.
To extend the most excellent process for the project team, the designers should appraise the submittal procedure and work with the rest of the project team. No extra liability should be put up on any single member by the project team and the communication should be smooth.
As the leaders of construction coordination, contractors and construction managers have a responsibility to encourage and facilitate the sharing and distribution of BIM technology on a project. They must also understand and convey the nature of the information that is being shared. Appropriate contract language that will foster the open sharing of BIM information must be developed. The contract language cannot alter the relationships of the project team members or change their responsibilities beyond their ability or what they are licensed to perform.
Design teams should assess the information required to execute code enforcement checks and permitting. All the project design and constructions are well-matched with community safety and smooth the progress of community development. The designers will always be in a position to accept new formats for demonstration of a project’s fulfillment with specified standards.
Owners should accept the responsibility of the costs related with BIM. Owners will have to be familiar with the additional deliverables (such as final as-built models) that constitutes added services.
Subcontractors convey the explanation of the design intent to the Design Team. Their work must be coordinated with that of other subcontractors by sharing the electronic information they have developed in file formats that can be utilized and combined with the work of others. They must support their software vendors to extend file formats to instantly exchange between the various trade subcontractors. Subcontractors also must ensure that all parties understand what they will supply as part of their contract and what will constitute additional work.
To get the full integrated BIM technology, software vendors will build up methods for the various project team to put in and maintain the data with regard to the specific characteristic of the project inside their responsibility. In a word the software industry should always contain the interoperability.
BIM should provide modification with the advancement of the design to incorporate the rising levels of detail characteristic of the various design stages—from schematic to construction documents at the suitable point in the design course.
Posted by Rajib Dey
Business Development
rajib@jobs2india.com
Global Associates (Pioneer Company in 3D modeling with BIM & Sketchup)
Monday, March 21, 2011
Architectural Desing & BIM
The architectural BIM is built up utilizing software applications for instance Revit, Archicad, Tekla and should be compatible with Navisworks software for integration into a single model for viewing and clash detection.
The architectural BIM developed all through the construction documents phase of the design will consist of all architectural elements for example building exterior skin, interior walls, doors, ceilings, casework, full height framing studs, overhead ceiling and equipment supports and compression posts.
The conceptual and schematic BIM must contain basic elements of the building skin to communicate primary design concepts to the LACC user and campus groups excluding wall framing, overhead supports, casework or detailed door elements.
Posted by Rajib Dey
Business Development
Global Associates (A pioneer company in BIM modeling service)
Visit us at www.bimoutsourcing.com
Wednesday, February 23, 2011
The Most Popular Aspect Of AEC Industry – BIM
The numerous advantages of BIM process makes it the most sought after tool in the AEC industry. Among the various other benefits of BIM, there are some key reasons which make it so popular. The most important reason is that it provides a good estimation during bidding and procurement. It also coordinates greatly in construction sequencing.
Another great advantage of BIM is to identify possible conflict. This is a great help to the contractor as any conflict in the structure can hamper the total project. Biggest advantage of using BIM is lesser amount of errors and hence rectifications which saves costs and resources of the contractor.
Another aspect of BIM behind its popularity is its capability to analysis the ‘what if’ condition. The construction sequencing option, shuffling of human resources, fine tuning cost factors are the important facet of the ‘what if’ analysis of BIM software. But the most important reason is that it gives both the creator and end users a chance to visualize the model virtually which gives a clear understanding of the end product. From the understanding the building owner can take informed decision about the proposed project. All these advantages along with some other make the BIM a most popular tool for the building construction industry.
Thursday, February 17, 2011
BIM is essential for Glazing Industry
Technical Glass products America is now applying various BIM technologiesfor creating models of its products and publishing. The firm has now modeled its full line of fire rated glazing products, framing systems, steel curtain wall, doors and windows including products, for instance, the Pilkington Profilit channel glass. Contract glazing firm ‘Trainor Glass Co.’ has also modeled several custom impact glass curtainwall systems successfully.
A large numbers of building products companies as well as curtain wall manufacturers, glass fabricators and component suppliers are creating their products in BIM and making BIM libraries for future application. This system will also provide assistance to building products companies for making their position better for getting architectural specification.
BIM will create a new collaborative IPD contracting form as this 3D modeling software will permit planners, designers, manufacturers, contractors, glazing subcontractors and owners to work from the similar object-related database.
With IPD and more design build, glass fabricators get the ability to inherit the design progression and support the BIM model as shop drawings. “Instead of the architects creating one set of models and the fabricators creating another set from that, they’re creating one set to meet both needs,” said EcoBuild America speaker Diane Davis.
Glass fabricators have the opportunity “to create virtual model catalogs, so their products work as little BIM sub-models that carry the manufacturers’ data, energy data and carbon footprint data,” Davis said. “These can be downloaded by architects and designers for their model.” “Fabricators should not create files for all the BIM programs as they did with CAD, but create their program with the IFC, or Industry Foundation Classes, an international open standard for BIM” she said.
“A standard glass manufacturer probably wouldn’t be interested in BIM, but would focus on green efforts and energy conservation” said EcoBuild America speaker Diane Davis, president, AEC Infosystems Inc., Baltimore. “Especially in today’s cap and trade scenario, if the glass manufacturers show the energy efficiency offset in the production of glass, it could become a green matrix within the industry and get connected with the green standards, like Energy Star and LEED [Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design] credits. That’s where the manufacturer would be asked for his input, which in turn would become part of the BIM data.”
Besides creating 3D models the BIM process can provide many vital information which will be very useful for glazing system suppliers and contract glaziers - wind loads, wind tunnel tests, structural live load movement requirements, material finishes, glass type, interlayer type, allowable deflection on framing systems, light transmission, thermal information, curtain wall profiles, test criteria, drift and earthquake requirements, sound transmission, fabrication part numbers, installation schedules, and field inspection data.
BIM can be applied to store and evaluate field record of glass and curtain wall data in an instinctive model which facilitates easy and smooth cost analysis of the glass for the owners and that hyperlink to field report documents. This feature permits BIM models to work as a 3D Web page of a building that connects to documents, plans, sketches and photographs.
BIM provides sustainable design by creating greater energy efficiency including thermal and structural analyses. The Glazing contractors will get the benefits to develop more sophisticated curtain wall systems.
With BIM model the glazing contractors can fix up fabrication and fit-up issues virtually and resolve it before built physically. This will also lead to diminish the misuse in time, material, field labor and enhance trade coordination with on-site materials.
Pinnacle Infotech has expertise in designing, drafting & modeling the curtain wall and glazing system through state of the art BIM and CAD software. Pinnacle generates different kinds of shop drawing including Aluminum Cladding Shop Drawings, Glass Entrance Shop Drawings, Curtainwall Shop Drawings, Rain Screen Cladding Shop Drawings, Window Shop Drawings, All other Glazing Shop Drawings. Pinnacle also offers 3D modeling services for glass and aluminum glazing systems, curtain wall and window wall etc.
Posted By:
Debarati Nath
Content Writer
Thursday, February 3, 2011
BIM(Building Information Modeling) provides great benefits to specialty contractors
With BIM the specialty contractors provide digital takeoff to run the digital estimate and digital prints providing the estimator and project managers to proficiently carry out takeoffs and collaborate across the entire scope of the project.
The specialty contractors can easily tie the data from BIM models to other programs for estimating and scheduling to connect the entire construction lifecycle.
BIM reduces the time to perform recurring calculations for specialty contractors and thus enhance profit & reduce risks.
The specialty contractors are able to create schedules, plans, and a bill of materials for building components.
The specialty contractors can slice up the project into smaller working parts and pieces with just one set of working drawings in the trailer.
By applying BIM the specialty contractors facilitate efficient paradigms for buyouts and estimating through the process of procurement and buying the material
With BIM the specialty contractors get positive returns on investment (ROI) in the technology. BIM can also bring benefits to the specialty contractors with respect to spatial interferences, visualization of electrical design, space use, trade coordination, and shop drawings submittal and review.
Posted by Rajib Dey
Business Development
rajib@jobs2india.com
3D modeling services
Saturday, January 8, 2011
BIM – A Grim concern over the Lack of Awareness
The 2010 Middle East Building Information Modelling Market Survey, conducted by buildingSMART ME, underlines this point. There is a significant lack of professionally-trained BIM users in the region, with the majority of respondents stating they had been self-taught. What this translates into is a low level of BIM expertise and competency in the region. The survey indicates that only 25% of respondents used BIM, while the figure is 36% in Western Europe and 49% in the
Typically, regional users will employ BIM for visualization, 3D co-ordination and 2D drawing extraction. But there are myriad other advantages, such as scheduling, cost estimation, construction management and even facilities management. Contractors and consultants need a clear developmental path to embrace BIM in its totality.
While the regional market may be seen to be inexperienced – and to some extent, insecure – in its adoption of such new technology, the survey did point out that there is strong awareness of BIM in the region and its value to construction. About 79% of respondents indicated some awareness of and/or exposure to BIM, citing its major selling points as reduction in design errors and improved quality control and productivity.
The major stumbling blocks to large-scale BIM adoption are availability of skilled staff (51%), cost of software (48%), cost of implementation (34%) and availability of training. The issue of cost will only be overcome if contractors and consultants begin to understand the return on investment in both increased productivity and added value.
It was clear that such a new-fangled concept had no place in the nuts, bolts and drawing-board environment of traditional contracting. Such attitudes are changing slowly as the construction industry becomes increasingly savvy in terms of deploying new technologies.
This is not to suggest that the road to BIM does not have its fair share of obstacles. Obviously no software package can replace a building-services coordinator whose 20 years of experience allows him to detect clashes on 2D drawings with uncanny intuitiveness.
What is needed is for such highly-skilled people to impart their knowledge to others. If you consider that the towering achievements of
Friday, December 31, 2010
BIM Software – a one stop solution for the Architect
BIM is more than just an acronym. For facility managers, Building Information Modeling software can be a powerful new tool to enhance a building’s performance and manage operations more efficiently throughout a building’s life.
What is BIM software? While definitions vary because the concept is still evolving, think of BIM software as a giant database. BIM software is intended to be a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility that forms a reliable basis for decisions during its life cycle, existing from earliest conception to demolition.
That doesn't mean that BIM software is the same as CAD programs. True BIM software encompasses more than a 3D computer-rendered model of the building. In addition to architectural information, the complete BIM contains all of the building’s information, from wall systems, structural systems, HVAC equipment, plumbing fixtures, door and window schedules, and finishes, right down to the manufacturer, supplier, and square footage of every material specified on the project.
The Benefits of BIM Software:
Cost savings are one of the biggest benefits to using BIM software. The majority of the life-cycle cost of a building does not come from the design and construction phase, but from operating the building over 20 to 50 years. Researches have shown that operations and maintenance account for between 60 and 85 percent of total costs of ownership.
For example, in 2004, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), commissioned a study to identify and estimate the efficiency losses in the U.S. capital facilities industry from inadequate interoperability among CAD, engineering, and software systems. The study quantified approximately $15.8 billion in annual costs of inadequate interoperability in the
Here's where BIM software can fix the problem. BIM software can be used as a database throughout the life of the building. It can generate as-built floor plans and elevations for tenant test fits and build-outs. It can recall the paint color of the accent wall in the executive conference room on the 11th floor, for example. Further, it can calculate the square footage of that same accent wall when a new executive comes on board and wants to change its color, so maintenance crews know how much paint is required.
By contrast, when a tenant wants to build out a space, the facility executive typically works from, or perhaps has to track down from the architect, a set of as-built drawings that may or may not be accurate, depending on the building’s age and how many tenants have occupied the space. Even worse, in the absence of as-built, facility executives end up re-drawing the space, wasting time and energy creating what would already have existed had there been a BIM model of the building. As BIM software has advanced, some applications have developed the ability to link relevant portions of the BIM to outside information sources, such as manufacturer specifications.
Thursday, December 30, 2010
The History of the BIM and the Success Story Till Date
Although Building Information Modeling (BIM) has its roots in the mid 1980s only recently has it risen in popularity within the Architectural, Engineering and Construction (AEC) industries. Due to this significant rise in popularity the AEC industry has created a demand for well trained individuals capable of implementing BIM technology in the work place. In an effort to meet these demands various sources have begun the process of introducing BIM-related resources to help facilitate the adoption of BIM technology. This popular aid of the AEC industry has its roots deep in the mid 1980’s.
In 1986 Graphisoft introduced their first “Virtual Building Solution” known as ArchiCAD (Kmethy, 2008). This revolutionary new software allowed architects to create a virtual, three dimensional (3D) representation of their project instead of the standard two dimensional (2D objects found in competing computer aided design (CAD) programs of the time. This was important because architects and engineers were then able to store large amounts of data sets ‘within’ the building model. These data sets include the building geometry and spatial data as well as the properties and quantities of the components used in the design.
In comparison, designers using standard CAD applications required countless specification sheets in order to convey all the required information pertaining to the project. The creation of a digitally constructed virtual building model, along with its associated data, is known as Building Information Modeling. Building Information Modeling (BIM) can be defined as the creation and use of coordinated, consistent, computable information about a building project in design – parametric information used for design decision making, production of high-quality construction documents, prediction of building performance, cost estimating and construction planning.
Since the BIM software architecture is based on parametric modeling the geometric consistency and integrity of the building model is maintained in spite of any changes or modifications that may have been made to it. Understanding the concept of these parametric objects is key to understanding what a building information model is and how it differs from traditional 2D design. A parametric object consists of a series of geometric definitions and their associated data and rules. In addition, these geometric definitions are integrated non-redundantly and do not allow for inconsistencies between the model and its associated data set. This means that any changes made directly to the model will result in an equal change to the data set associated with the model.
Although BIM technology is still relatively new, initial experiences indicate that the creation of a 3D model with associated information reduces errors of design, improves design quality, shortens construction time, and significantly reduces construction costs (Eastman, 2003). Due to these initial findings the popularity of BIM has grown tremendously in the past decade, and as the popularity of BIM increases so too has the demand for well trained designers and construction managers with proficiency in the use of BIM technology.
Tuesday, December 21, 2010
Pennsylvania State University Wins Autodesk BIM Experience Award University Honored for Extensive Use of Building Information Modeling in Architecture
According to Robert Holland, associate professor of architecture and architectural engineering, "Autodesk Revit software products are
The university began integrating Autodesk BIM solutions into its curricula since 2004. The software now serves two colleges and three departments: the Architecture and the Landscape Architecture departments in the
Autodesk software used by the university's architecture, landscape architecture and architecture engineering students includes: Autodesk Revit Architecture Autodesk Revit Structure Autodesk Revit MEP AutoCAD Civil 3D Autodesk 3ds Max Design Autodesk Ecotect Analysis Autodesk Green Building Studio Autodesk Navisworks products AutoCAD.
About
Saturday, December 18, 2010
Reasons to Use BIM
When the contractor will start to do a construction work there are many stages which he has to pass by before ground breaking. And Building Information Modeling or BIM is one of the most important factors in this stage. With the help of it, AEC industry gets a huge advantage not only in the preconstruction stage but also in the construction stage of the project. The benefit list of Building Information Modeling is almost endless. Here we will discuss the reasons of choosing Building Information Modeling in the project.
The success of any project lays in the clear understanding among the architects, engineers, construction professional, facility manager and building owners. The BIM can bridge the void and help them to communicate successfully. With the help of this wonderful tool, they are able in providing consistent and reliable information across the scope of a project.
BIM is an integrated process that vastly improves project understanding and allows for predictable outcomes. This visibility enables all project team members to stay coordinated, improve accuracy, reduce waste, and make informed decisions earlier in the process—helping to ensure the project’s success. Building Information Modeling supports the continuous and immediate availability of project design scope, schedule, and cost information that is high quality, reliable, integrated, and fully coordinated.
Among the many competitive advantages it confers are:
• Increased speed of delivery that means time saved
• Better coordination that indicates fewer errors
• Decreased costs for which money save for building owner and increase profit of the architects
• Greater productivity helps the architect to keep the quality of work in good standard
• Higher-quality work will deliver to the clients
• New revenue and business opportunities will open both for architect and building owners
For each of the three major phases in the building lifecycle—design, construction, and
Management — Building Information Modeling offers access to the following critical information:
- In the design phase—design, schedule, and budget information
- In the construction phase—quality, schedule, and cost information
- In the management phase—performance, utilization, and financial information
The ability to keep this information up to date and accessible in an integrated digital environment gives architects, engineers, builders, and owners a clear overall vision of their projects, as well as the ability to make better decisions faster—raising the quality and increasing the profitability of projects. Although building information modeling is an approach and not a technology, it does require suitable technology to be implemented effectively.
Examples of some of these technologies, in increasing order of effectiveness, include:
• CAD
• Object CAD
• Parametric Building Modeling
In this way, from this blog you came to know what Building Information Modeling is, how it confers competitive advantages, how it can be achieved using a flexible range of technologies and how various BIM software can help firms that want to investigate and implement this exciting new approach. That’s why the modern AEC industry prefers BIM technology in the construction project.
